To gain a better understanding of breast cancer it is important to understand how any cancer can develop. When genes responsible for regulating the growth of cells and keeping them healthy, mutate or experience abnormal changes, cancer can develop. Genes are found in each cell’s nucleus and when operating normally the cells in our bodies follow an orderly process where the new healthy cells replace the old ones as they die out. Over time, abnormal changes or mutations can turn on certain genes and turn off others in a cell. When cells experience these mutations, the orderly process of normal cell growth is disrupted and the cells can continue to keep dividing without following the control of order, they produce more of the same cells and ultimately form a tumor.
There are two forms of tumors; benign and malignant tumors. Benign tumors are not dangerous to health or considered cancerous because their cells are close to normal in appearance, slow growing, are not invasive to nearby tissues, and they don’t spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors on the other hand are cancerous and left unchecked the cancerous cells can spread beyond the original tumor to other parts of the body.
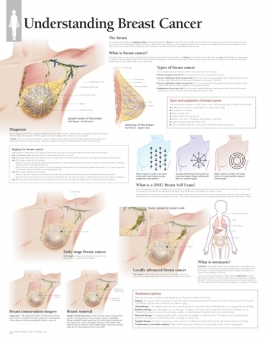
Breast cancer is a malignant tumor that has developed from cells in the breast. The normal breast is comprised of lobes and lobules (milk-producing glands), milk ducts (tiny tubes that carry the milk from the lobules to the nipple), and the stroma (fatty tissue and connective tissues surrounding the ducts and lobules, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels). Breast cancer usually begins in the lobules (lobular cancers) or the ducts (ductal cancers), although it can begin in the stromal tissues of the breast.
Breast cancers can spread through the lymph system, this occurs when cancerous cells invade healthy breast tissue and make their way into the underarm lymph nodes (small organs that filter out foreign substances in the body). Once a cancer cell has made it into the lymph nodes, the cancerous cells have a pathway to spread beyond the original tumor and onto other parts of the body. Breast cancer stages (expressed as a number on a scale of 0 through IV) refer to how far the cancerous cells have spread beyond the original tumor.
Genetic abnormalities or a mistake in the genetic material is the cause of breast cancer. Inherited genetic abnormalities are only responsible for 5-10% of cancers, while genetic abnormalities resulting from the aging process and everyday life are responsible for 85-90% of breast cancers.
These are some examples of steps everyone can take for staying as healthy as possible which may have some impact on your risk of getting breast cancer.
- Eat a balanced diet
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Avoid tobacco products
- Exercise regularly
While taking these steps to live a healthier lifestyle they may have some impact on your risk of getting breast cancer but they cannot eliminate the risk. Learn more about how you can manage breast cancer risk factors and the importance of monthly breast self-exams (BSE) as well as annual screening tests (mammograms). Johns Hopkins Medical center states “Forty percent of diagnosed breast cancers are detected by women who feel a lump, so establishing a regular breast self-exam is very important.” [ www.hopkinsmedicine.org/avon_foundation_breast_center/treatments_services/breast_cancer_screening/breast_self_exam.html ] Mammograms are important in helping detect cancer before you can feel a lump, breast self-exams help you become familiar with how your breasts look and feel so you can alert your healthcare professional if there are any changes.

Leave a Reply