Protecting healthcare personnel from infectious disease exposures in the workplace requires a combination of controls. The use of PPE is one of four key components in the hierarchy of healthcare worker safety programs.
- Training (e.g. policies and procedures)
- Engineering Controls (e.g. negative pressure rooms)
- Work Practice Controls (e.g. not recapping needles)
- Personal Protective Equipment
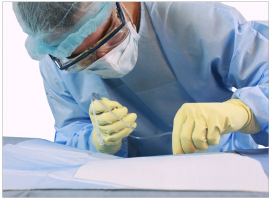
Although PPE is listed last in the hierarchy of prevention, it is extremely important for protecting healthcare workers from disease transmission. Listed below is a sampling of some commonly found types of PPE found in healthcare settings.
- Gloves (protect hands)
- Gowns/aprons (protect skin and clothing)
- Masks (protect mouth/nose)
- Respirators (protect respiratory tract from airborne infectious agents)
- Goggles/glasses (protect eyes)
- Face shields (protect face, mouth, nose and eyes)
- Shoe covers (protects from airborne infectious agents)
- Head covers/bonnets (protects from airborne infectious agents)
The type of PPE used will vary based on the level of precautions required; standard and contact, droplet or airborne infection isolation. When selecting PPE it is important to consider three things; type of exposure anticipated, durability and appropriateness for the task, and fit. Remember to always use safe work practices to protect yourself and limit the spread of contamination. Polices may vary by facility, please check with the appropriate department director in your facility for more information.

Leave a Reply